Star Plots allow you to compare multiple variables. You can compare any number of variables to see how they may or may not relate to one another. Radii (half a diameter of a circle), represent each plotted variable. The proper name for a radii in a Star Plot is equi-angular spoke. It is a way of showing multivariate data.
The graph shown is a Star Plot of Motor Trend Cars seven rating areas. The areas that are being rated: disp, cyl, mpg, qsec, draf, hp. The larger the area is on the Star Plot, the greater the amount of the variable.
http://addictedtor.free.fr/graphiques/graphcode.php?graph=63
Sunday, November 13, 2011
Correlation Matrix
Correlation Matrix is a symmetric square matrix which displays the relationship between a set of data. The same data set is listed on the vertical and horizontal axis.
The graph shown is a Correlation matrix of twenty variables.
http://wiki.eigenvector.com/index.php?title=Tools_CorrelationMap
The graph shown is a Correlation matrix of twenty variables.
http://wiki.eigenvector.com/index.php?title=Tools_CorrelationMap
Similarity Matrix
Similarity Matrixes show the similarity between variables. There is a line that goes across the greatest length of the graph that shows 100% similarity. This line seems inevitable no matter what you are graphing. Squares are used to create, generally a cube, as to what will be representing the data, The squares size, color, shading, or/and pattern could vary to show the similarity or difference between the variables.
The graph shown is a Similarity Matrix of “Correlation matrices for two polymers showing similarity relationships among pairs of conformations.”
http://www.renci.org/~sthakur/
The graph shown is a Similarity Matrix of “Correlation matrices for two polymers showing similarity relationships among pairs of conformations.”
http://www.renci.org/~sthakur/
Stem & Leaf Plot
Stem & Leaf Plots help show the distribution of a selected group of numbers or values. Generally this graph is used for two digit numbers but can be used for any number of digit values. The last digit in each number is shown on the right side of the Stem & Leaf plot. The first digit(s) are shown on the left side of the Stem & Leaf Plot. If it is a three digit number being plotted, then the first two digits will be on the left side of the stem and the last digit on the right. This type of graph helps show repeated numbers and patterns between numbers. If numbers are not integers, they are rounded.
The graph shown is a Stem & Leaf Plot listing the "Ages of People at Family Reunion." The ages of the people taken from the Stem & leaf Plot: 1, 8, 9, 32, 34, 37, 45, 51, 55, 81. So I would guess there was one grandparent, three grandchildren, and six siblings.
http://www.eduplace.com/math/mhm/5/06a/index.html
The graph shown is a Stem & Leaf Plot listing the "Ages of People at Family Reunion." The ages of the people taken from the Stem & leaf Plot: 1, 8, 9, 32, 34, 37, 45, 51, 55, 81. So I would guess there was one grandparent, three grandchildren, and six siblings.
http://www.eduplace.com/math/mhm/5/06a/index.html
Box Plot
Box Plot is also known as Box and Whisker Diagram. In this graph the beginning of the box represents the 25th percentile and the end of the box represents the 75th percentile, the line inside the box marks the meridian or 50th percentile. The whisker part of this graph can represent a few different values: minimum and maximum, the 10th and 90th percentiles, one standard deviation above and below the mean, and any other statistical value of importance relating to the shown data.
The graph shown is a Box (Box and Whisker) Plot of "Guinea Pigs' Tooth growth." This Box Plot shows the relationship between Tooth Length and Vitamin C dose in mg. The shading of the boxes indicates how the Vitamin C dose was given. Yellow indicates Ascorbic Acid and orange indicates Orange Juice. The horizontal axis shows the Vitamin C dose. The vertical axis shows Tooth Length.
http://sphaerula.com/legacy/R/boxplotTwoWay.html
The graph shown is a Box (Box and Whisker) Plot of "Guinea Pigs' Tooth growth." This Box Plot shows the relationship between Tooth Length and Vitamin C dose in mg. The shading of the boxes indicates how the Vitamin C dose was given. Yellow indicates Ascorbic Acid and orange indicates Orange Juice. The horizontal axis shows the Vitamin C dose. The vertical axis shows Tooth Length.
http://sphaerula.com/legacy/R/boxplotTwoWay.html
Histogram
Histograms are similar to bar charts but with one crucial difference. The bars in a bar chart show their value by the height, whereas, in a Histogram the width of the bars relates to its value and the height refers to the frequency of the value. In a bar chart each bar represents a different category while its height represents the frequency the category comes up. In a Histogram each bar represents the same category but indicates the value or range of values by its placement along the horizontal axis and its occurrences by its height relative to the vertical axis. Easy way to depict the two graphs is that a bar chart’s bars will have space between them and a Histogram’s bars usually don’t.
The graph shown is a Histogram of “Distribution of salaries of the Acme Corporation.” The Horizontal axis displays the salary ranges of the employees in thousands. The vertical axis displays the number of employees that earn a salary in the salary ranges.
http://www.statcan.gc.ca/edu/power-pouvoir/ch9/histo/5214822-eng.htm
The graph shown is a Histogram of “Distribution of salaries of the Acme Corporation.” The Horizontal axis displays the salary ranges of the employees in thousands. The vertical axis displays the number of employees that earn a salary in the salary ranges.
http://www.statcan.gc.ca/edu/power-pouvoir/ch9/histo/5214822-eng.htm
Parallel Coordinate Graph
Parallel Coordinate Graphs are drawn on a vertical graph with a connected set of points plotted at each of the vertical intervals. Points are only plotted on the parallel vertical lines. Theses point are referred to as Vertexes which is defined as a corner or intersection with regards to a line. These points are connected in between the parallel lines by polylines which are a connected series of line segments.
The graph shown is a Parallel Coordinate Graph of cell variations based on nine DNA strands. The parallels are the nine DNA strands. The lines represent different cells and their relationship to the nine DNA variations.
Triangular Plot
Triangular Plots show three variables in the form of a Triangle. Each side of the triangle is represented by a variable. There are line intervals that run parallel to each side of the triangle. Certain parallels may be significant and sometimes none of them will be significant. A point is plotted according to its three variables. The greater the percentage of one variable means the less a percentage is for another variable. All three cannot equal their highest value. The three variables plotted will sum up to equal a constant.
The graph also displays isolines and coloring to enhance the differences or similarities of the plotted points with regards to the three sediments.
http://www.rockware.com/product/featuresLobby.php?id=165&category=368
The graph shown is a Triangular Plot of Feldspar, Muscovite, and Quartz compositions. The more like Quartz a point is the less like Feldspar it is. The more like Feldspar a point is the less like Muscovite it is. The more like Muscovite the point is the less like Quartz it is.
http://www.rockware.com/product/featuresLobby.php?id=165&category=368
Windrose
Windrose shows the frequency of wind direction in a given area. Generally, given as a percentage of how much the wind has blown in the direction.
The graph shown is a Windrose of Heathrow in England. The wind blows mostly from the South-Southwest, and the least from the South-Southeast and Southeast. The change in color between yellow and blue show the change in the interval.
http://www.metoffice.gov.uk/climate/uk/so/print.html
The graph shown is a Windrose of Heathrow in England. The wind blows mostly from the South-Southwest, and the least from the South-Southeast and Southeast. The change in color between yellow and blue show the change in the interval.
http://www.metoffice.gov.uk/climate/uk/so/print.html
Climograph
Climograph shows the relationship of temperature to precipitation according to each month. Temperature is show as line similar to one on a line graph. The bar graph depicts precipitation per month.
The graph shown is a Climograph of cities in Africa, Mexico, and Australia. The red lines indicate changes in temperature relative to the bar graph at the base of the map.
http://wps.prenhall.com/esm_mcknight_physgeo_8/22/5645/1445185.cw/content/index.html
The graph shown is a Climograph of cities in Africa, Mexico, and Australia. The red lines indicate changes in temperature relative to the bar graph at the base of the map.
http://wps.prenhall.com/esm_mcknight_physgeo_8/22/5645/1445185.cw/content/index.html
Population Profile
Population Profiles are best represented as Population Pyramids. Population Pyramids show the age, gender, number, The graph has the ability to show birth rates, death rates, population decline, population increase, or population. Males are on the left and females are on the right. The horizontal axis shows number of people. The vertical axis shows the age of the population.
The graph shown is a Population Profile in the form of a pyramid. The Population Pyramid is of Poland in 2010. As you can see, the population is wavering. The reason for wavering like this is the same throughout most of Europe. The World Wars affect the populations greatly. The indentation at the age of 40 is probably because their parents were from the World War II era. The new indentation is probably forming because people are having fewer children in Europe all the time.
http://www.d-transition.info/countries-glance-3/poland-208/
The graph shown is a Population Profile in the form of a pyramid. The Population Pyramid is of Poland in 2010. As you can see, the population is wavering. The reason for wavering like this is the same throughout most of Europe. The World Wars affect the populations greatly. The indentation at the age of 40 is probably because their parents were from the World War II era. The new indentation is probably forming because people are having fewer children in Europe all the time.
http://www.d-transition.info/countries-glance-3/poland-208/
Scatterplot
Scatterplot plots each observation as a point on the graph. A trend line is generally plotted with the scatter plots. The trend line can indicate whether there is a positive or negative relationship between the observations. Positive meaning both variables are increasing; negative meaning on variable increases while the other decreases.
The graph show is a Scatterplot graph of "Earthquake magnitude and Depth Data." The occurrences are plotted based on the Latitude and Longitude that they occur on. The Magnitude is shown by the size of the dot. The depth is defined by the color of the dot.
http://www.originlab.com/index.aspx?go=Products/Origin/Graphing/Line/Symbol
The graph show is a Scatterplot graph of "Earthquake magnitude and Depth Data." The occurrences are plotted based on the Latitude and Longitude that they occur on. The Magnitude is shown by the size of the dot. The depth is defined by the color of the dot.
http://www.originlab.com/index.aspx?go=Products/Origin/Graphing/Line/Symbol
Index Value Plot
Index Value Plot has an index value versus an absolute number such as zero. Zero could be the index value if it is a relevant vase number. An average number could be the index value. Everything starts from the index value in middle of the graph. More than one variable according to some median.
The graph shown is an Index Value Plot of “Commercial Real Estate, Housing & Equity REITS (Oct 1993 – Jan 2008).” The horizontal axis displays each year from 1993 until 2008 during the month of October. The vertical axis displays the Index value intervals. The Index value that the four lines begin from appears to be around 100.
http://seekingalpha.com/article/75069-commercial-real-estate-still-in-fairly-good-shape
The graph shown is an Index Value Plot of “Commercial Real Estate, Housing & Equity REITS (Oct 1993 – Jan 2008).” The horizontal axis displays each year from 1993 until 2008 during the month of October. The vertical axis displays the Index value intervals. The Index value that the four lines begin from appears to be around 100.
http://seekingalpha.com/article/75069-commercial-real-estate-still-in-fairly-good-shape
Accumulative Line Graph (Lorenz Curve)
Accumulative Line Graph (Lorenz Curve) shows the information’s actual distribution against a line that shows equal distribution. The curve in the graph is called Lorenz Curve.
The graph shown is an Accumulative Line Graph (Lorenz Curve) of The world’s most and least equal societies with regards to income. The blue indicates perfect equilibrium while anything below is less than perfect. Namibia in the green has the least equal society with a small percentage of people holding the wealth.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Lorenz_curve_of_Denmark,_Hungary,_and_Namibia.png
The graph shown is an Accumulative Line Graph (Lorenz Curve) of The world’s most and least equal societies with regards to income. The blue indicates perfect equilibrium while anything below is less than perfect. Namibia in the green has the least equal society with a small percentage of people holding the wealth.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Lorenz_curve_of_Denmark,_Hungary,_and_Namibia.png
Bilateral Graph
Bilateral Graph is a line graph with two related variables represented by their own line. This graph shows the relationship between the two variables and the relationship can show additional information.
The graph shown is a Bilateral Graph of "Average Sale Price – Single Family Detached" homes each month. Each line represents the price of a different year. Bilateral graph usually only depict two variables but you can added as many as need to show your point.
http://www.marketvitalsigns.com/
The graph shown is a Bilateral Graph of "Average Sale Price – Single Family Detached" homes each month. Each line represents the price of a different year. Bilateral graph usually only depict two variables but you can added as many as need to show your point.
http://www.marketvitalsigns.com/
Nominal Area Choropleth Map
Nominal Area Choropleth Maps use qualitative classification with no implicit ordering. Nominal is one level of data measurement in maps; Ordinal, interval, and ratio are the other forms. Qualitative is a none numerical grouping system and information is grouped according to category.
The map Shown is a Nominal Area Choropleth Map of "Largest Ancestry, 2000." It gives no indication of value but simply states the dominate Ancestry of each county.
http://skyeome.net/wordpress/?p=187
The map Shown is a Nominal Area Choropleth Map of "Largest Ancestry, 2000." It gives no indication of value but simply states the dominate Ancestry of each county.
http://skyeome.net/wordpress/?p=187
Unstandardized Choropleth Map
Unstandardized Choropleth Maps are not areal averaged but simply stated as is. This type of mapping usually results in data being misread and chaotic.
The map shown is an Unstandardized Choropleth Map of "Europe Forest Area" per country. The lighter the color green the less forest area there is. The darker the color green the more forest area there is. Because the map is unstandardized we cannot tell where the forests lie. We only know the percentage of area that is covered.
http://blog.mapsofworld.com/2011/10/
The map shown is an Unstandardized Choropleth Map of "Europe Forest Area" per country. The lighter the color green the less forest area there is. The darker the color green the more forest area there is. Because the map is unstandardized we cannot tell where the forests lie. We only know the percentage of area that is covered.
http://blog.mapsofworld.com/2011/10/
Standardized Choropleth Map
Standardized Choropleth Maps are areal averaged based on an areal unit. An areal unit can be a county, country, or standardized area. There are two main ways to areal average: by Density or by Percentage.
The map shown is a Standardized Choropleth Map of "Salve Population Density." It is standardized because it is areally average based on a determined areal unit. The areal unit in this map is modern county limits. Many United States maps are standardized by counties.
http://www.city-data.com/forum/general-u-s/189474-what-northernmost-southern-city-southernmost-northern-7.html
The map shown is a Standardized Choropleth Map of "Salve Population Density." It is standardized because it is areally average based on a determined areal unit. The areal unit in this map is modern county limits. Many United States maps are standardized by counties.
http://www.city-data.com/forum/general-u-s/189474-what-northernmost-southern-city-southernmost-northern-7.html
Univariate Choropleth Map
Univariate Choropleth Maps show only one variable by using colors, shading, symbols, or patterns. Is a basic choropleth Map.
The map shown is a Univariate Choropleth Map of "Leading Church Bodies, 2000." It is a Univariate map because only the dominate church body is shown; no other variable is defined within the map.
http://bigthink.com/ideas/21289?page=all
The map shown is a Univariate Choropleth Map of "Leading Church Bodies, 2000." It is a Univariate map because only the dominate church body is shown; no other variable is defined within the map.
http://bigthink.com/ideas/21289?page=all
Bivariate Choropleth Map
Bivariate Choropleth Maps show two different variables on one map by using colors, shading, symbols, or patterns. Generally, lines are used to show the second variable; whether they are vertical, horizontal, angular lines and/or colored. Shading is usually used for the main/base information.
The map shown is a Bivariate Choropleth Map of "Percent Change, 1990 to 2000 and Population Density, 1990." The different colors show the 3 ranges of people per square mile in 1990. The lighter to darker shading represent the population change from a loss to unnumbered gain.
http://www.personal.psu.edu/cab38/GEOG321/14_multivariate02/multivariate.html
The map shown is a Bivariate Choropleth Map of "Percent Change, 1990 to 2000 and Population Density, 1990." The different colors show the 3 ranges of people per square mile in 1990. The lighter to darker shading represent the population change from a loss to unnumbered gain.
http://www.personal.psu.edu/cab38/GEOG321/14_multivariate02/multivariate.html
Unclassed Choropleth Map
Unclassed Choropleth Maps do not use ranges or classes to determine color shading. Instead it goes from lightest to darkest shade and has a lowest and highest number. There is one range and the variable is shaded according to where it falls on the shading scale. This type of map is similar to the Continuously Variable Proportional Circle Maps but it uses shading, colors, and patterns of aerial units versus varying circle sizes.
The map shown is an Unclassed Choropleth Map of "Population Density" of people per square km. It is an Unclassed map because the shading varies on the number of people per square mile not a range of people per square mile.
http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=116
The map shown is an Unclassed Choropleth Map of "Population Density" of people per square km. It is an Unclassed map because the shading varies on the number of people per square mile not a range of people per square mile.
http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=116
Classed Choropleth Map
Classed Choropleth Maps are maps that use specific ranges or classes that are used to help classify aerial units. These types of maps can be compared to Range Graded Proportional Circle Maps because they both have a set number of ranges. The difference between the two is Classed Choropleth Maps use shading, colors, and patterns of aerial units versus varying circle sizes. Counties are commonly used as an aerial unit. There are four classes: equal steps, quantiles, natural breaks, and minimum variance.
The map shown is a Classed Choropleth map of the "Percent English, 2000." It is a Classed map because colors are attributed to arbitrary ranges that were determined by one of the four classing systems. The darker the color, the higher the percentage of people with English heritage; the lighter the color the lower, the percentage of people with English heritage.
http://blogreadersblog.blogspot.com/2008/11/americans-with-english-ancestry-vote.html
The map shown is a Classed Choropleth map of the "Percent English, 2000." It is a Classed map because colors are attributed to arbitrary ranges that were determined by one of the four classing systems. The darker the color, the higher the percentage of people with English heritage; the lighter the color the lower, the percentage of people with English heritage.
http://blogreadersblog.blogspot.com/2008/11/americans-with-english-ancestry-vote.html
Range Graded Proportional Circle Map
Range Graded Proportional Circle Maps are Proportional Circle Maps that have a set number of circles used. This is different from Continuously Graded Proportional Circle Maps in that Range Graded has a set number of circles versus Continuously Graded has no set number of circles.
The map shown is a Range Graded Proportional Circle map of Violent Crimes in the USA. You can tell this a Range Graded Proportional Circle Map versus Continuously Variable because the circle sizes have been given value ranges versus a single number. This map also has an Added variable in the form of a pie chart. The variable is a positive (orange shading) or negative (blue shading) change in Violent Crimes. The different shading in the pie chart indicates the type of Crime and percent change that it holds in that state.
http://thesocietypages.org/graphicsociology/2009/02/17/typical-crime-map-victimization/
The map shown is a Range Graded Proportional Circle map of Violent Crimes in the USA. You can tell this a Range Graded Proportional Circle Map versus Continuously Variable because the circle sizes have been given value ranges versus a single number. This map also has an Added variable in the form of a pie chart. The variable is a positive (orange shading) or negative (blue shading) change in Violent Crimes. The different shading in the pie chart indicates the type of Crime and percent change that it holds in that state.
http://thesocietypages.org/graphicsociology/2009/02/17/typical-crime-map-victimization/
Continuously Variable Proportional Circle Map
Continuously variable Proportional Circle maps are Proportional Circle Maps with an added variable in the form of a pie chart in each circle. The circles vary in size with no set number of sizes. The pie chart information differences are represented with colors, shading, or patterns.
The map shown is a Range Graded Proportional Circle Map of European Forestry Production by Country , 2006. While there are Circle sizes show with indicated numbers, they are there as a reference. There are more than 4 circle sizes found in the map. You can tell this is a Continuously Proportional Circle Map because the circles are not assigned ranges but one number.
The map shown is a Range Graded Proportional Circle Map of European Forestry Production by Country , 2006. While there are Circle sizes show with indicated numbers, they are there as a reference. There are more than 4 circle sizes found in the map. You can tell this is a Continuously Proportional Circle Map because the circles are not assigned ranges but one number.
The map shown is a Continuously Variable Proportional Circle Map of Forest and Woodland and are in percent of Total Land per country in Africa. The green shading indicates the percentages of each country that is covered by forest and woodland. The pie charts tell how much of the percentage is woodland versus forest. Yellow indicates woodland and red indicates forest.
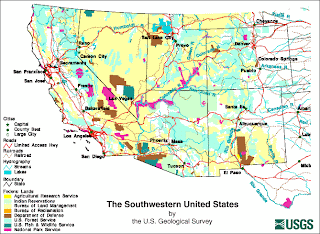
DOQQ
Digital Orthophoto Quarter Quads (DOQQ) are aerial photos with geometric map qualities used by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). The aerial photos are adjusted to eliminate distortion before the adding of the qualities, this is called orthorectification. The DOQQs are georectified as well.
The map shown is a Digital Orthophoto Quarter Quads (DOQQ) Map of San Francisquito Creek Watershed. This map was created to help determine how to resolve an overflow problem in the area. The shading is to help show specific areas that need attention.
http://geography.wr.usgs.gov/sfcreek/maplayout.html
The map shown is a Digital Orthophoto Quarter Quads (DOQQ) Map of San Francisquito Creek Watershed. This map was created to help determine how to resolve an overflow problem in the area. The shading is to help show specific areas that need attention.
http://geography.wr.usgs.gov/sfcreek/maplayout.html
DEM
Digital Elevation Model (DEM), also known as Digital Terrain Model (DTM), is a digital view of Earth’s topography used by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). This model uses the raster data format to create 3D images or colorized maps to display elevation.
The map shown is a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Map of Crater Lake National Park. This particular DEM uses 3D imagery to show the elevation in the National Park. The bottom right image is a DRG of Crater Lake.
http://docs.autodesk.com/MAP/2011/ENU/AutoCAD%20Map%203D%202011%20Help/Map3D_2011_HTML_Help/filesBestPracticesForGeoData/WS1a9193826455f5ff-75c1f7c3124f51ccbd1-49e2.htm
The map shown is a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Map of Crater Lake National Park. This particular DEM uses 3D imagery to show the elevation in the National Park. The bottom right image is a DRG of Crater Lake.
http://docs.autodesk.com/MAP/2011/ENU/AutoCAD%20Map%203D%202011%20Help/Map3D_2011_HTML_Help/filesBestPracticesForGeoData/WS1a9193826455f5ff-75c1f7c3124f51ccbd1-49e2.htm
DLG
Digital Line Graphs (DLG) are used by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) to show a variety of information using the vector data format and georectification. Vector data format is similar to a point and line map. These Graphs can show topography, hydrography, boundaries, roads, and utility lines.
The map shown is a Digital Line Graph (DLG) Map displaying Federal Land types. The map is similar to a thematic map but it is created using a vector data format and georectification by the USGS therefore it is extremely accurate.
http://geochange.er.usgs.gov/sw/resources/sw_basemap/
The map shown is a Digital Line Graph (DLG) Map displaying Federal Land types. The map is similar to a thematic map but it is created using a vector data format and georectification by the USGS therefore it is extremely accurate.
http://geochange.er.usgs.gov/sw/resources/sw_basemap/
DRG
Digital Raster Graphics (DRG) are a topographic map image from the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) that uses the raster data format. Raster data format uses a grid system to place data on a map. These images are scanned and georectified by the USGS. Georectification means that Latitude and Longitude coordinates have been attached to a map.
The map shown is a Digital raster Graphics (DRG) map of Yellowstone. It is a topographic map with contour lines that has been scanned and georectified by the USGS.
http://www.topoquest.com/map-detail.php?usgs_cell_id=48367
The map shown is a Digital raster Graphics (DRG) map of Yellowstone. It is a topographic map with contour lines that has been scanned and georectified by the USGS.
http://www.topoquest.com/map-detail.php?usgs_cell_id=48367
Isopleth
Isopleth Maps are used to show lines that cannot be measured at a specific point but rather over an area. These types of maps are not defined by a predetermined area. Isopleth Maps and Isoline Maps are fundamentally the same and the names are used interchangeably.
The maps shown are an Isopleth maps of ocean tidal movements. The lines connect points of equal tidal movements. The lines are enhanced by different color shading.
The maps shown are an Isopleth maps of ocean tidal movements. The lines connect points of equal tidal movements. The lines are enhanced by different color shading.
Isopach
Isopach are maps that use isolines to connect points that have the same rock or sediment thickness. The term Isopach can be used interchangeably with isoline when the map is representing rock or sediment thickness.
The map shown is an Isopach Map showing the "Total Sediment Thickness of the World’s Oceans & Marginal Seas" in meters. The map connects the points of equal sediment thickness.. The lines are enhanced by different color shading. The darker the color (blues) the thinner the sediment; the light the color (reds) the thicker the sediment.
http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/sedthick/sedthick.html
The map shown is an Isopach Map showing the "Total Sediment Thickness of the World’s Oceans & Marginal Seas" in meters. The map connects the points of equal sediment thickness.. The lines are enhanced by different color shading. The darker the color (blues) the thinner the sediment; the light the color (reds) the thicker the sediment.
http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/sedthick/sedthick.html
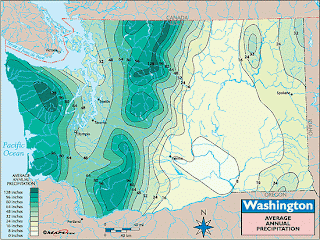
Isohyet
Isohyets are maps that use isolines to connect points that have the same amount of rainfall or precipitation. The term Isohyet can be used interchangeably with Isoline when the map is representing rainfall or precipitation.
The map shown is an Isohyet Map showing the "Washington Average Annual Precipitation". The map connects the points of equal precipitation. The lines are enhanced by teal shading. The lighter the color the less precipitation falls annually in that area; the darker the color the more precipitation falls annually in that area.
http://qnhn.wordpress.com/
The map shown is an Isohyet Map showing the "Washington Average Annual Precipitation". The map connects the points of equal precipitation. The lines are enhanced by teal shading. The lighter the color the less precipitation falls annually in that area; the darker the color the more precipitation falls annually in that area.
http://qnhn.wordpress.com/
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)